15 Most Dangerous Malware Of All Time
Over the years, numerous of malicious software, or malware for short, have caused all kinds of damage across computers from all over the world. Here are some of the most dangerous malware in the history of computers. To read about different kinds of malware, click here.
1. Zeus
Also known as Zbot, Zeus is a notorious Trojan which infects Windows users and tries to retrieve confidential information from the infected computers. Once installed, it tries to download configuration files and updates from the Internet. Zeus has the ability to steal information and attack banking and financial institutions around the world. Zeus is created and customized using a Trojan-building toolkit, which is available online for cybercriminals. Using the retrieved information, cybercriminals log into banking accounts and make unauthorized money transfers through a complex network of computers.
The Trojan was first identified in 2007 and has since been reduced to remnants. However, it has made a reemergence through installations of ransomware threats and spearphising campaigns associated with Dropbox. Zeus is exploited as an inexpensive and easy-to-use toolkit for hackers and remains this way today. It is known by many names including PRG and Infostealer. To date, Zeus has already infected more than 3.6 million systems in the United States. In 2009, security analysts found that Zeus has spread on more than 70,000 accounts of banks and businesses including the Bank of America and NASA.
2. Zeus Gameover (P2P) (Zeus Family)
This malware is just one of the many variants of the Zeus family. This type of malware relies on a peer-to-peer botnet infrastructure. The generated peers in the botnet can act as independent Command and Control servers and are able to download commands or configuration files between them, finally sending the stolen data to the malicious servers.
Zeus Gameover is used by cybercriminals to collect financial information by targeting various user data from credentials, credit card numbers, and passwords to any other private information which might prove useful in retrieving a victim’s banking information. The malware is estimated to have infected 1 million users around the world.
Other malware from the Zeus family include SpyEye, Ice IX, Citadel, Carberp, Bugat, Shylock, and Torpig.
3. Conficker
The Conficker has been dubbed as a serious worm infection for Windows computers. First identified in 2008, it has been known for its aggressive attacks to disable antivirus and anti-spyware applications and then further infect systems. Specialized anti-malware tools had to be created to combat Conficker and ultimately remove it from infected computers. Many systems infected with Conficker were considered lost due to control of the computer being taken over by remote attackers.
4. CryptoLocker
The CryptoLocker has made its name well known in the short time it has been around. The CryptoLocker is a ransomware threat that virtually locks down an infected system and does not permit usage or limited use until necessary actions are taken, such as removing CryptoLocker or entering a paid-for key code. Encryption of files was one of CryptoLocker’s major destructive actions, corrupting files and installed applications on an infected computer.
5. Qakbot
The Qakbot acts as a botnet that steals passwords and attaches itself to file shares to spread. This malware threat first emerged in 2011, making its rounds to connect to Command and Control servers waiting for instructions to carry out malicious actions on infected computers. These instruction sets provide the Qakbot the tasks of stealing login information, which then could be used by remote attackers to infiltrate online accounts such as banking accounts. A recent resurgence was noticed in September 2014 where it has so far conducted some of its well-known malicious activities.
6. Sykipot
The Sykipot is a backdoor Trojan horse threat that dates back to 2007 and has had its ups and downs in its ability to bypass two-factor authentication. Such authentication measures are highly targeted in recent password-related breaches which led to massive amounts of data being stolen. The Sykipot is emerging once again and showing up in new targets, such as civil aviation and smart cards.
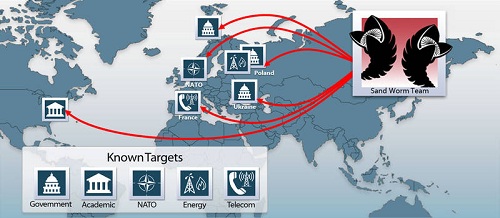
7. Sandworm
The Sandworm has been a mysterious malware threat as it has just recently made its presence well known. Although some researchers claim that it has been around as early as 2009. The Sandworm is a type of document-based malware threat that has a powerful vector for targeted attacks. The Microsoft Office has been targeted by Sandworm, highly similar to how other threats have long-attacked Adobe documents. The Sandworm uses a very effective zero-day exploit that happens to affect any version of Windows since Vista. The Sandworm is also believed to have evolved in its short lifespan to associate with socially-engineered methods to entice users to open an infected document, which will then execute its malicious code.
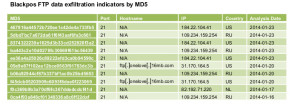
8. BlackPOS
The BlackPOS is a point-of-sale malware targeting credit and debit card data swiped at POS systems running MS Windows systems. This malware was created by an individual who identifies as the “Antikiller”. The BlackPOS disguises itself as a known AV vendor software to avoid being detected in POS systems. It uses RAM scraping to grab card data from the memory of the infected POS device and exfiltrates collected data to a compromised server then uploads it to a file transfer protocol (FTP). The BlackPOS is designed to bypass Firewall software and is only 207 kilobytes in size. The crimeware kit costs $1800-$2300. Its known victims include customers of major US banks such as Chase, Capital One, Citibank, Union Bank of California, and Nordstrom Debit.
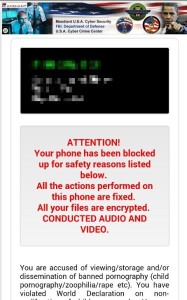
9. KOLER
First spotted in 2014, the KOLER is an android Trojan extorting mobile device users for money to unlock their data. The Trojan poses as a valid video player that offers premium access to pornography. The KOLER automatically downloads during a browsing session. After the drive-by Trojan infects a machine, it prevents the user from accessing mobile home screens and displays a bogus message purporting to be from the national police service. The message claims the user has been accessing child abuse websites and demands payment to escape prosecution.
10. ILOVEYOU
The ILOVEYOU virus is considered to be one of the most infectious computer viruses ever created. The virus managed to wreak havoc on computer systems all over the world, causing damages totaling an estimate of $10 billion. The virus was so powerful that governments and large corporations were forced to take their mailing system offline to prevent infection. The e-mail attachment disguised itself as a .txt file. However, once clicked, the ILOVEYOU virus will send itself to everyone in the mailing list and proceed to overwrite all computer files with itself, making the computer unbootable.
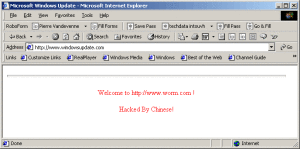
11. Code Red
The Code Red worm was first spotted in 2001 when it was discovered by two eEye Digital Security employees. The name was coined from the Code Red Mountain Dew that they were drinking at the time they discovered the worm. The worm targeted computers with Microsoft IIS web server installed, exploiting a buffer overflow problem in the system. The worm barely leaves any trace on the hard disk because it is able to run entirely on memory, with a size of just 3569 bytes. Once infected, the Code Red worm will proceed to make a hundred copies of itself but, due to a bug in its programming, will duplicate even more and end up eating a lot of the system’s resources.
The Code Red worm launches a denial of service (DoS) attack on several IP addresses (including the White House website) and allows backdoor access to the server, allowing remote access to the machine. The most memorable symptom of the said worm is a message left behind on affected web pages which says, “Hacked By Chinese!” A total of 1-2 million servers were affected and the worm caused more than $2 Billion in lost productivity.
12. Melissa
This virus was named after an exotic dancer from Florida. The virus was created by David L. Smith in 1999. The virus started as an infected Word document that was posted up on the alt.sex UseNet group, claiming to be a list of passwords for pornographic sites. The virus mails itself to the top 50 people in the user’s email address book which causes an increase of email traffic and disruption of the email services of governments and corporations. Melissa also corrupts documents by inserting a The Simpsons reference into them.
Smith served a total of 20 months in prison and paid a fine of $5000. The virus reportedly caused $80 million in damages.
13. Stuxnet
An example of a virus created for the purpose of cyberwarfare, the Stuxnet is believed to have been created by the Israeli Defense Force together with the American Government. It was created with the intention to disrupt the nuclear efforts of the Iranians. The Stuxnet managed to ruin a fifth of Iran’s nuclear centrifuges and nearly 60% of infections were concentrated in Iran. The Stuxnet was designed to attack industrial Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC), which allows for automation processes in machinery, and was specifically aimed at those created by Siemens. The virus was spread through infected USB drives. Although Siemens eventually found a way to remove the malware from their software.
14. Mydoom
The Mydoom is a worm for Windows that became one of the fastest spreading email worms since the ILOVEYOU virus. The author remains to be unknown but is believed to have been paid to create the said worm because it contains the text message, “andy; I’m just doing my job, nothing personal, sorry,” The worm was named by McAfee employee Craig Schmugar. The name was coined from “mydom”, a line of text in the program’s code which means my domain, and the word “doom” because of the dangers the worm posed. The Mydoom spreads itself by appearing as an email transmission error and contains an attachment of itself. Once executed, the worm sends itself to email addresses that are in the user’s address book and copies itself to any P2P program’s folder to propagate itself through that network.
The payload itself is a twofold: first, it opens up a backdoor to allow remote access and second, it launches a denial of service attack on the controversial SCO Group. It is believed that the worm was created to disrupt SCO due to conflict over ownership of some Linux code. The Mydoom caused an estimate of $38.5 billion damages. The worm is still active in some form today.
15. Flashback
The Flashback is a Trojan and is one of the few Mac malware to have gained notoriety as it showed that the Mac isn’t immune to such attacks. It was first discovered in 2011 by an antivirus company Intego as a fake Flash install. In order for the Trojan to work, the user simply needs to have Java enabled. (But who doesn’t have their Java enabled, right?) The Trojan propagates itself by using compromised websites containing JavaScript code that will download the payload. Once installed, the Mac becomes part of a botnet of other infected Macs. The good news is that, if it’s infected, it’s localized to that specific user’s account meaning the Trojan doesn’t spread anywhere else. The bad news is that more than 600,000 Macs were infected.
As of 2014, an estimate of 22,000 Macs have been infected. Oracle published a fix for the exploit with Apple releasing an update to remove Flashback from people’s Mac.